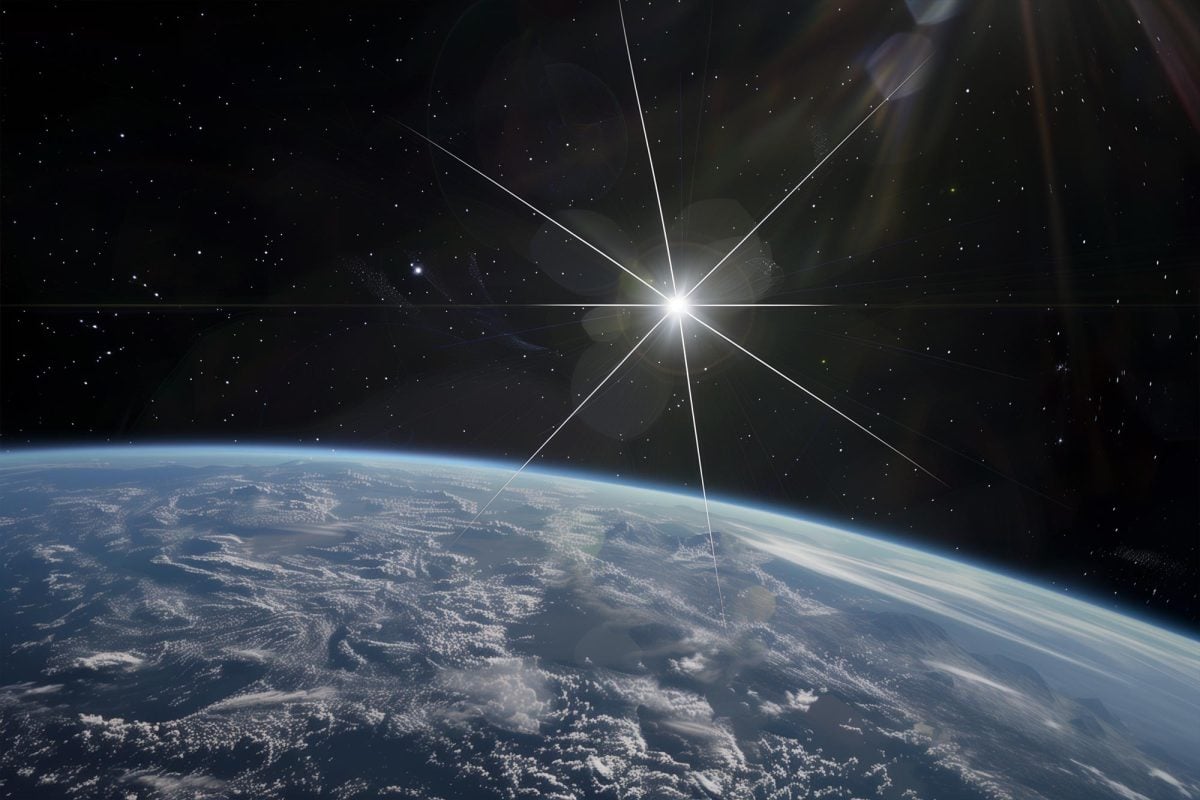
NASA, in collaboration with George Mason University, is gearing up for a groundbreaking space mission that could reshape our understanding of the universe. The $19.5 million Landolt NASA Space Mission, named after renowned astronomer Arlo Landolt, aims to deploy an artificial star in Earth’s orbit. This innovative project is designed to refine telescope calibrations and astrophysical measurements, paving the way for significant advancements in understanding the universe’s expansion, stellar properties, and dark energy.
Mission Highlights: Unveiling Cosmic Secrets
Artificial Star Launch: Slated for 2029, the mission will place an artificial star—equipped with eight precision lasers—in geostationary orbit 22,236 miles above Earth. This position ensures the star remains stationary relative to the Earth’s surface, allowing continuous calibration for ground-based telescopes.
Precise Stellar Brightness Calibration: By emitting a known photon rate, the artificial star will enable astronomers to create more accurate stellar brightness catalogs, aiding in the measurement of nearby stars and distant supernovae.
Improving Telescope Accuracy: The mission tackles challenges caused by atmospheric filtration, ensuring ground telescopes can measure light with unprecedented precision.
The Science Behind the Mission
Astrophysical research relies heavily on accurately measuring stellar brightness and photon emissions. Current methods leave room for error, limiting our ability to understand phenomena like dark energy, which drives the universe’s expansion.
Peter Plavchan, the mission’s principal investigator and associate professor of physics and astronomy at George Mason University, emphasizes the importance of these advancements:
“When we look at a star with a telescope, no one can tell you today the rate of photons or brightness with the desired level of accuracy. This mission will change that, achieving measurements accurate to 0.25%.”
The project also seeks to refine parameters related to exoplanet habitability and stellar evolution, offering new insights into whether life-sustaining conditions exist elsewhere in the universe.
Collaboration and Innovation
This first-of-its-kind university-led NASA mission involves a diverse team of collaborators:
Academic Partners: Institutions like the University of Florida, University of Hawaiʻi, and California Institute of Technology will contribute expertise in astrophysics and engineering.
Technological Expertise: The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) will oversee photon emission measurements, ensuring laser calibration accuracy.
Student Involvement: George Mason University students from the College of Science and College of Engineering and Computing will actively participate in designing and building the payload, gaining invaluable hands-on experience.
Revolutionizing Astrophysics and Beyond
The Landolt NASA Space Mission is not just about technological achievement—its potential scientific impact is profound.
Refining Dark Energy Studies: By achieving precise flux calibration, the mission will enhance our ability to measure the speed and acceleration of the universe’s expansion.
Exoplanet Research: Improved data will redefine the search for habitable zones and provide critical insights into planetary systems beyond our solar system.
Stellar Properties: Better measurements of surface temperatures, brightness, and stellar composition will advance our understanding of stellar lifecycles.
As NIST’s Susana Deustua explains, precision is the cornerstone of astronomy:
“We constantly ask: ‘How big? How bright? How far?’ Accurate answers require precise measurements and excellent instrument characterization.”
A Leap Toward Cosmic Discovery
Mission control, based at George Mason University’s Fairfax Campus, represents a significant milestone for the institution and its partners. This collaboration underscores the role of academia and science in pushing the boundaries of human knowledge.
The Landolt NASA Space Mission is a testament to innovation, promising to answer fundamental questions about the cosmos and inspire the next generation of astrophysicists. With its ambitious goals and collaborative framework, this mission is set to redefine how we perceive the universe, unlocking mysteries that have puzzled humanity for centuries.
Let’s gear up for a new era of space exploration and scientific discovery!
This SEO-optimized article incorporates keywords like “NASA mission,” “artificial star,” “dark energy,” “George Mason University,” and “astronomical measurements” to enhance online visibility. Let me know if you’d like to refine or target specific subtopics further!




















+ There are no comments
Add yours