Diet drinks have long been marketed as a healthier alternative to sugary beverages, helping people cut calories and manage weight. However, new research suggests that these zero-calorie drinks might actually make you hungrier. If you’re wondering why you still feel cravings even after sipping on your favorite diet soda, science has some answers.
The Science Behind Diet Drinks and Hunger
Many diet drinks use artificial sweeteners such as aspartame, saccharin, and sucralose to replicate the taste of sugar without the calories. However, recent studies indicate that these artificial sweeteners can disrupt the body’s natural appetite regulation, potentially leading to increased hunger and food intake.
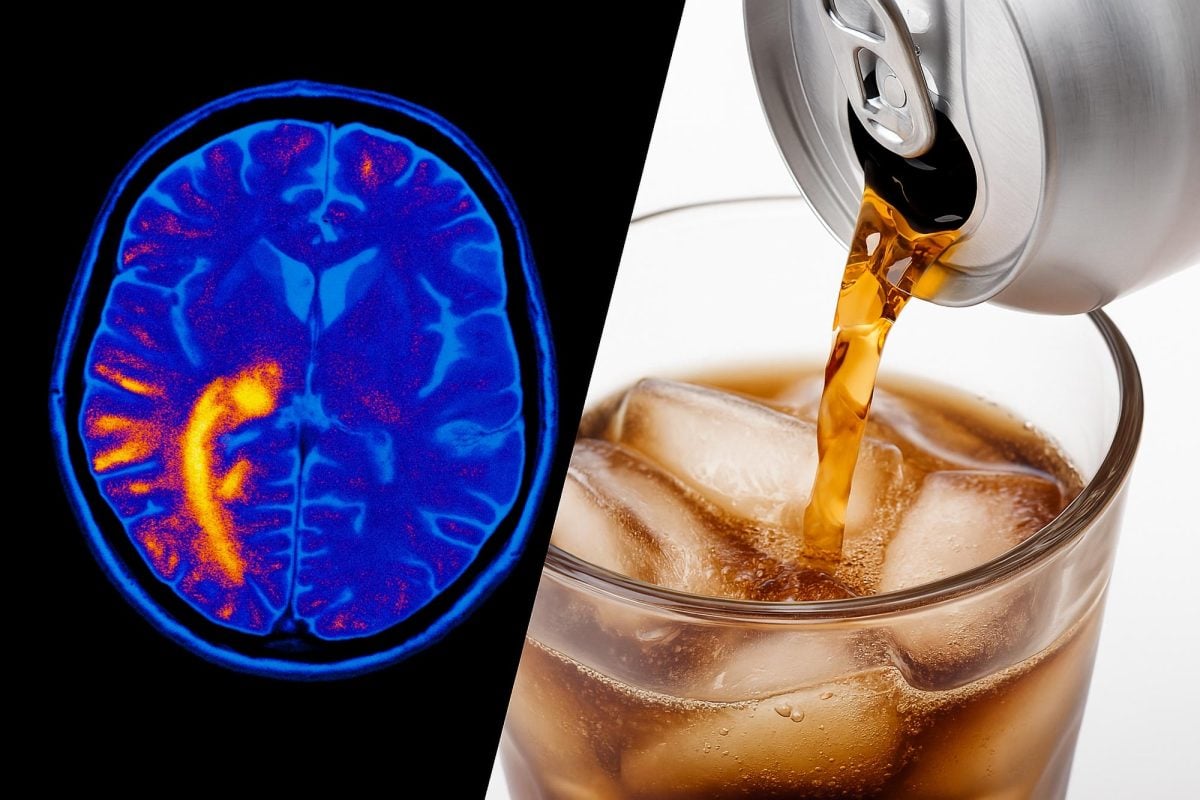
A study published in JAMA Network Open found that consuming sucralose may activate hunger-related regions in the brain, particularly in women and individuals with obesity. Researchers discovered that the artificial sweetener stimulates the hypothalamus, a brain region responsible for appetite control, making the body expect actual sugar intake. When the expected calories don’t arrive, the body may compensate by triggering cravings for high-calorie foods.
How Diet Drinks May Lead to Overeating
Misleading the Brain – Artificial sweeteners trick the brain into expecting sugar, leading to increased hunger and cravings.
Impact on Gut Hormones – Some artificial sweeteners may interfere with gut hormone signaling, reducing the feeling of fullness.
Changes in Gut Microbiota – Research suggests that artificial sweeteners can alter gut bacteria, which plays a crucial role in digestion and metabolism.
Increased Sweet Preferences – Regular consumption of diet drinks may heighten the preference for sweet foods, making it harder to resist sugary treats.
Blood Sugar Fluctuations – Some artificial sweeteners may cause insulin spikes, leading to drops in blood sugar levels that can trigger hunger.
The Debate Around Artificial Sweeteners
While some experts argue that artificial sweeteners can be beneficial for weight management by reducing overall calorie intake, others believe their long-term effects on metabolism and hunger are concerning. The World Health Organization (WHO) has recently advised against using non-sugar sweeteners for weight control, citing potential risks.
Additionally, the impact of artificial sweeteners may vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience increased hunger, while others may not notice significant changes in their appetite. Factors such as genetics, gut microbiome composition, and overall diet quality can play a role in how the body responds.
What Can You Do?
If you’re relying on diet drinks to cut calories but find yourself constantly hungry, consider these healthier alternatives:
Infused Water – Add slices of fruit or herbs to water for a refreshing, naturally flavored drink.
Herbal Teas – These provide warmth and flavor without artificial sweeteners.
Sparkling Water – Carbonated water with a splash of lemon or lime can satisfy soda cravings without added chemicals.
Natural Sweeteners in Moderation – If you need sweetness, consider honey or stevia in moderation.
Balanced Eating Habits – Focus on consuming nutrient-dense meals with adequate protein, fiber, and healthy fats to regulate appetite.
Final Thoughts
While diet drinks may seem like a great way to avoid sugar and excess calories, emerging research suggests they could backfire by making you hungrier. If weight management is your goal, focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods and natural hydration options may be a better long-term strategy. As always, moderation is key, and being mindful of your body’s hunger cues can help you make healthier choices.
As the conversation around artificial sweeteners continues, staying informed and making dietary choices based on how your body reacts will help you find the best approach to maintaining a healthy lifestyle.




















+ There are no comments
Add yours