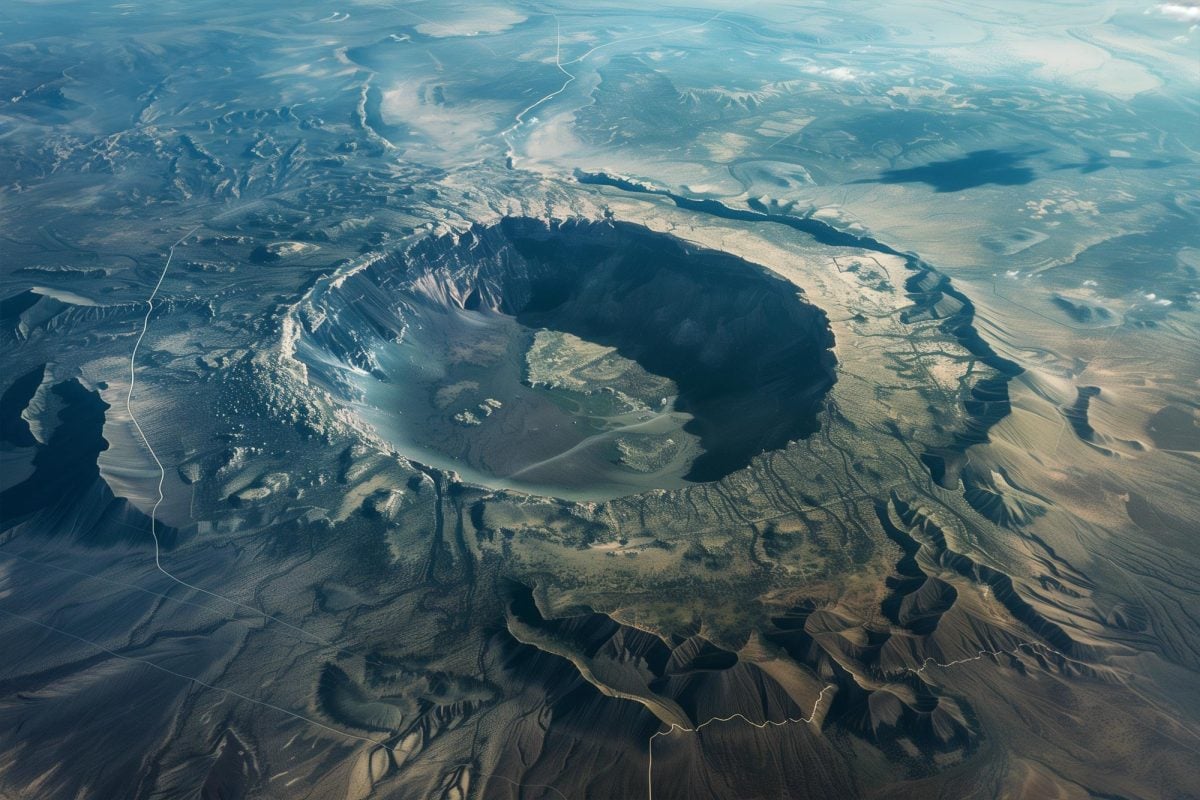
A groundbreaking discovery in Australia has reshaped our understanding of Earth’s ancient past. Scientists have identified a 3.5 billion-year-old meteorite crater, making it one of the oldest known impact sites on the planet. This finding provides new insights into Earth’s early environment, meteorite activity, and the role of extraterrestrial impacts in shaping our planet’s history.
A Landmark Discovery in Earth’s Geological Record
The crater, located in a remote region of Western Australia, was identified through geochemical analysis and satellite imaging. Researchers found evidence of shocked minerals and impact-generated structures, confirming that a massive meteorite struck the Earth billions of years ago.
Key Highlights of the Discovery:
✅ Estimated Age: 3.5 billion years
✅ Location: Western Australia
✅ Size: Potentially several kilometers in diameter
✅ Evidence: Shocked quartz, impact melt rocks, and geophysical anomalies
This discovery challenges previous assumptions about early Earth’s geological activity and suggests that meteorite impacts played a crucial role in shaping the planet’s crust.
Why Is This Discovery Important?
The newly discovered crater offers significant insights into several scientific areas:
1. Understanding Earth’s Early Environment
During the Archean Eon (4 to 2.5 billion years ago), Earth’s surface was vastly different from today. The discovery of this impact crater provides direct evidence of ancient meteorite collisions, helping scientists reconstruct early atmospheric and geological conditions.
2. Clues About Life’s Origins
Many scientists believe that meteorite impacts may have delivered essential organic compounds that contributed to the emergence of life. This crater could offer valuable clues about how meteorites influenced the development of early life forms.
3. Rewriting Geological Timelines
Previously, the oldest confirmed impact structures were around 2 billion years old. This 3.5-billion-year-old crater significantly extends the known timeline of major meteorite impacts, providing fresh perspectives on Earth’s early geological evolution.
How Was the Crater Identified?
Scientists used a combination of field studies, satellite imaging, and isotopic dating to confirm the crater’s age and impact origins. Key indicators of an ancient impact included:
🔬 Shocked quartz grains – A signature of high-energy impacts.
🧪 Geochemical traces of extraterrestrial elements – Evidence of a space-born object.
🌍 Magnetic anomalies – Distortions in Earth’s magnetic field linked to ancient meteorite strikes.
What’s Next for Research?
This discovery has opened new doors for planetary scientists and geologists. Researchers are now planning:
More extensive field studies to map the full extent of the crater.
Advanced dating techniques to refine its age and impact history.
Comparisons with lunar and Martian craters to understand how similar impacts shaped other celestial bodies.
Final Thoughts
The discovery of a 3.5 billion-year-old meteorite crater in Australia is a monumental breakthrough in Earth sciences. It not only redefines our understanding of ancient meteorite impacts but also raises new questions about the role of space collisions in Earth’s history.
As researchers continue their investigations, this crater may hold the key to unlocking long-lost secrets of our planet’s early years—and perhaps even the origins of life itself.




















+ There are no comments
Add yours